As a pet parent, it’s important to recognize the signs and symptoms of common dog diseases. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking veterinary help as soon as possible can protect the community and even save your dog’s life. Here is the ultimate guide about common dog diseases and parasites that can impact your dog.

Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease (CIRDC)
CIRDC, more commonly known as Kennel Cough, is a common illness that is transmitted dog to dog through airborne droplets.
Symptoms: The main symptom of CIRDC is a persistent, forceful cough. It often sounds like a “honking” noise. Some dogs may show other symptoms of illness, including sneezing, a runny nose, or eye discharge.
Incubation Period: Ranges from 2 to 14 days
Treatment: Rest is the best treatment. Veterinarians may prescribe antibiotics if they think it is bacterial.
Recovery: While resting, use a dog-safe humidifier to help with your dog’s upper respiratory infection. Most importantly, avoid any type of interaction with other dogs for two weeks to prevent the spread.
Fitdog policy: Complete antibiotics and a 2 week quarantine from the first day of symptoms before returning to daycare.
How to Prevent: Stay current on vaccines including bordetella, parainfluenza and adenovirus and canine coronavirus.
Interesting Fact: “Kennel Cough” is a catch all phrase for upper respirator disease and is caused by various bacterial and viral infections. Young dogs (especially puppies) and elderly appear to be the most severely affected. Read More: 6 Kennel Cough Facts Every Pet Parent Should Know

Giardia
Giardiasis is an intestinal infection caused by a microscopic protozoan parasite called Giardia duodenalis.
Symptoms: Vomiting, diarrhea, belching and gas. There also may be blood or mucus in the stool. Signs may be severe or the pet may have mild symptoms such as on and off diarrhea or occasional nausea.
Incubation Period: The time it takes from ingestion of cysts to passage in feces is 5 to 12 days.
Treatment: The most common drugs used to kill Giardia are fenbendazole and metronidazole. Treatment typically lasts three to ten days.
Recovery: With proper medicine, Giardia can be eliminated within two weeks. However, Giardia cysts can cling to your dog’s fur and reinfect the pet when it licks itself. Make sure to give your dog a thorough bath while they are in the treatment period to prevent reinfection.
Fitdog policy: Complete medication, 3 weeks from start of medication, entrance bath.
How to Prevent: Refresh your dog’s water bowl often and keep them away from water that is near feces.
Interesting Fact: A pet becomes infected with Giardia by swallowing the cyst stage of the parasite. Licking or smelling the stools of other pets or drinking contaminated water easily spreads them.

Tapeworms
Tapeworms are an intestinal parasite that are flat, segmented worms and can be found in dogs, cats, humans and many other species.The most common tapeworm species is Dipylidium Caninum
Symptoms: There’s no obvious symptoms, but look out for you dog licking or biting at their anus and scooting their bottom. Also, you may see what looks like a small piece of rice around your dog’s anus or in their poop. For more severe infections, weight loss or vomiting may occur.
Incubation Period: If your dog lives in a flea-infested area, infection may occur in as little as two weeks.
Treatment: Tapeworms in dogs are treated with a parasiticide drug called praziquantel. Praziquantel is sold over the counter or prescribed. Always speak to your veterinarian before giving your dog any medication.
Recovery: The product will work quickly, and the tolerance in canines is very positive.
Fitdog policy: Complete medication, letter from the vet indicating dog is no longer contagious.
How to Prevent: The best way to avoid a tapeworm infestation is to keep your dog free of flea infestation. Since 90% of the fleas life cycle exists outside of its host, that means ridding your house and yard of fleas.
Interesting Fact: Unlike other intestinal parasites, dogs cannot become infected by eating fertilized tapeworm eggs. Tapeworms must first pass through a flea before they can infect a dog.

Fleas
Symptoms: Intense itching, extensive skin damage, biting, licking, or scratching. Also, keep an eye out for flea “dirt”; tiny dark specks that look like dirt, but are actually flea feces.
Incubation Period: There are four stages in the life cycle of a flea: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. It takes at least one or two months until all the life cycle stages have run through their course.
Treatment: Treat the adult fleas living on your pet with flea and tick shampoo, sprays, dips, spot-on medications or prescription flea and tick treatments from your veterinarian.
Recovery: An infestation may take between six weeks and three months to eliminate. To prevent re-infestation, wash all dog beds and soft dog toys in hot, soapy water. Meanwhile, wash your own bed and vacuum all flooring, furniture, and anywhere else your dog frequently lays.
How to prevent: Flea preventatives kill fleas that come in contact with your dog but they do not provide a protective force field. To truly combat fleas, clean your dog’s belongings and house and spray down your landscaping around your home.
Fitdog policy: Take flea preventative medication and receive a flea bath before returning to daycare.
Interesting Fact: 90% of fleas life cycles are outside of your dog (that means they are living in your house or yard).

Ticks
Symptoms: Licking and chewing; red, inflamed skin; pale gums and lethargic; scabs; head shaking.
Incubation Period: Tick-borne disease can be transmitted within 3 – 6 hours of a tick bite.
Treatment: Use a pair of fine-point tweezers to remove a tick. To remove, gently pull straight upward, in a slow, steady motion. This will prevent the tick’s mouth from breaking off and remaining embedded in the skin. After disposing of the tick, gently clean the site of tick attachment with soap and water.
Recovery: Improved health usually begins within 24 hours and most dogs are completely recovered within 72 hours.
How to Prevent: Keep your dog on flea and tick prevention year-round. There are very effective oral prescription products available, including Nexgard and Bravecto, that will provide great protection against fleas and ticks. For over-the-counter prevention, Frontline Plus or a Seresto collar are also an option.
Fitdog policy: Take flea & tick medication and make sure all ticks are removed before returning to daycare.
Interesting Fact: Ticks aren’t just a problem outdoors. The brown dog tick is capable of completing its entire lifecycle indoors.
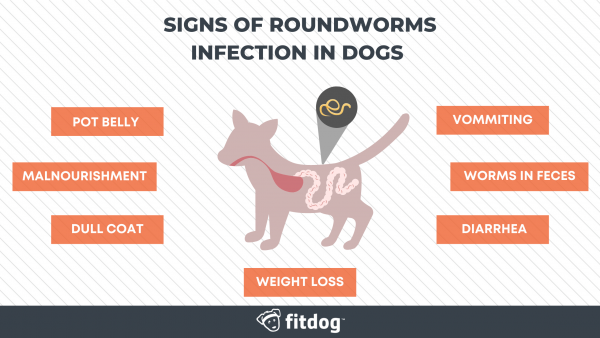
Roundworms
Roundworms, also known as ascarids or nematodes, are common parasites that live inside your dog’s intestines and feed on partly digested food.
Symptoms: Potbelly, diarrhea, vomiting, weight loss, malnourishment, weakness and a dull coat.
Incubation period: About 4-6 weeks. It can take a month after ingesting for the roundworm to lay eggs in the stool.
Treatment: Deworming drugs are very effective and there are a variety of oral deworming drugs that are available to kill the adult roundworm.
Recovery: The recovery process can take up to 4 weeks.
How to prevent: Many monthly heartworm preventives contain medications that are effective against intestinal roundworms and help prevent future infections. In addition, remove your dog’s feces as soon as possible to prevent the spread and transmission of roundworms.
Fitdog Policy: Complete medication and return with clear fecal exam.
Interesting Fact: Puppies get roundworms from their mother in utero.

Canine Respiratory Coronavirus
Canine respiratory coronavirus (CRCoV) is a group 2 coronavirus. It is genetically related to the bovine coronavirus and the human coronavirus.
Symptoms: Most dogs have mild symptoms consisting of cough, sneezing, and nasal discharge. However, some dogs can have an infection with no symptoms, yet still be able to transmit it to other canines.
Incubation Period: 1 to 4 days.
Treatment: There is no specific treatment for CRCoV. At this time, there is no vaccine to prevent CRCoV infection or reduce the clinical disease.
Recovery: Since CRCoV is highly contagious, isolation of infected dogs is necessary to minimize spread of infection. Estimated quarantine is 3 weeks.
How to prevent: Even though there is no vaccine for CRCoV, dogs should be vaccinated against other respiratory pathogens. Vaccines available include parainfluenza virus, adenovirus, distemper virus, and Bordetella bronchiseptica.
Fitdog policy: Letter from the vet that it is safe to return.
Interesting Fact: Sometimes vets can’t tell the difference between coronavirus and kennel cough.
Canine Flu
Canine influenza (CI), or dog flu, is a highly contagious viral infection affecting dogs and also cats.
Symptoms: Persistent cough, nasal discharge, sneezing, lethargy and anorexia.
Incubation Period: 1 to 5 days.
Treatment: It is highly recommended to see a veterinarian. Although there is no cure, your vet may require supportive care such as fluids and anti-inflammatory medications.
Recovery: Most dogs recover from canine influenza within 2-3 weeks, but should be isolated for 4 weeks to prevent the spread of the disease.
How to prevent: The virus can survive in the environment for up to 2 days, but is easily killed by disinfectants. Therefore, cleaning and disinfection consistently will help reduce the risk of virus transmission.
Fitdog policy: Letter from vet that it is safe to return; usually 4 weeks after isolation period.
Interesting Fact: It is a relatively new disease discovered and is being watched by public health officials.
Lepto
Leptospirosis is a rare zoonotic disease. Infected animals spread Lepto by through urine in soil and water. Recently, Lepto has made it’s way from wildlife to urban life.
Symptoms: Dehydration, diarrhea, extreme thirst, eye inflammation, lethargy, loss of appetite, nosebleeds and blood-tinged vomit, stool, urine or saliva.
Incubation Period: 5 to 15 days.
Treatment: If caught early on, it is easily treatable with antibiotics. For severe cases, dogs with severe kidney or liver damage may require hospitalization for intravenous fluid treatment and other therapy.
Recovery: When treated early and aggressively, the chances for recovery are good but there is still a risk of permanent residual kidney or liver damage.
How to prevent: The Leptospirosis vaccine will keep your dog immune to the disease and help prevent the spread.
Fitdog policy: Completed medication, have no symptoms and are vaccinated against Lepto.
Interesting Fact: Lepto is a zoonotic disease, which means it can be transmitted from animals to humans. Humans experience flu-like symptoms but it can lead to kidney or liver failure if left untreated.

Having a sick dog is never fun. Prevention and awareness are key to keeping them healthy and safe. If your dog shows any signs or symptoms related to these dog diseases and parasites, contact your veterinarian immediately.
Most importantly, keep your dog isolated at home if they develop any of these symptoms. Keeping them away from other dogs will prevent the spread of the dog diseases.
Sources:
VCA, AKC, AVMA, Drake Center.